Bloodborne Pathogen Information
Background
Confidential Information
Exposure to Blood/What to Do
Mandated Training
Hepatitis Vaccination
Handwashing
Biohazard Waste, Sharps Containers
Cleaning Procedures
MCPS Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan
Bloodborne Pathogen Information
Bloodborne pathogens are defined as pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to, hepatitis B virus (HBV) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). All blood and other potentially infectious materials will be handled as if contaminated by bloodborne pathogens. When differentiation between body fluids (if they contain blood) is difficult or impossible, all body fluids will be considered potentially infectious materials.
Maryland Occupational Safety and Health (MOSH) Standard 29 CFR 1910.1030 requires employers to establish a control plan to eliminate or minimize employee exposure to bloodborne pathogens. Information from MCPS Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Guidelines is provided below.
Information regarding individuals who have been diagnosed with HIV is confidential, and this information must remain confidential. It is a violation of one’s privacy to inform school staff, students, and/or the community of an individual who is HIV positive or who has auto immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) without the permission from the individual, or in the case of a minor, permission from a parent/guardian.
Ensure employee notifies his/her supervisor immediately.
- Have immediate supervisor call in a “First Notice of Loss” to CorVel (Montgomery County claims reporting program) at 1-888-606-2562.
- Contact appropriate staff to clean up blood spills using universal precautions and a bloodborne pathogens clean-up kit.
- Have appropriate staff dispose of blood-contaminated waste in the red biohazard box located in the school health room.
- When the red biohazard box is full, have the school health nurse contact Biomedical Waste Services, Inc. at 1-800-660-6581 for waste disposal pick-up and a replacement biohazard box and red bag (and lid, if needed).
- Have the employee contact the MCPS-contracted clinic listed below (within 24 hours) to receive a post-exposure medical evaluation and follow-up interview.
- tru HealthNow (formerly Medical Access), 12321 Middlebrook Road, Germantown, Maryland 20874, 301-428-1070
- Have the employee complete MCPS Form 230-33: Bloodborne Pathogens Post-Exposure Report, as soon as possible. The form should be provided to the examining physician. Additional copies must be provided, within five days of the incident, to the Employee and Retiree Service Center (ERSC) and Systemwide Safety Programs. The employee must also provide the examining physician MCPS Form 230-34: Health Care Professional's Written Opinion Form, which must be sent to Systemwide Safety Programs by the physician.
Mandated Bloodborne Pathogen Training
Annual online training must be completed by designated employees, including all teachers and other school-based employees, with the potential for occupational exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials. Required online bloodborne pathogen exposure prevention courses are available through SafeSchools. When designated employees log in to their SafeSchools training home page, assigned safety courses will appear in the 'Mandatory Training' section. The online bloodborne pathogen courses replace all previous VHS and DVD-based training. Additional information about completing online training is available on the Online Safety Training page.
All employees required to receive bloodborne pathogen exposure prevention training are offered, but not required to receive, Hepatitis B vaccinations, at no cost. To receive the vaccine, employees must submit MCPS Form 230-32: Hepatitis B Virus Vaccination Authorization Form to Systemwide Safety Programs. After authorization is received, employees may contact the MCPS-contracted clinic listed below for vaccination. Employees who received vaccination 10 or more years ago from an MCPS-contracted clinic should make an appointment with this clinic to receive a titer test. This test will determine if a booster vaccination is necessary.
- tru HealthNow (formerly Medical Access), 12321 Middlebrook Road, Germantown, Maryland 20874, 301-428-1070
All employees required to receive bloodborne pathogen exposure prevention training who decline to receive the Hepatitis B vaccination are required to submit MCPS Form 230-31: Mandatory Hepatitis B Virus Vaccination Declination Statement to Systemwide Safety Programs for compliance with MOSH regulations.
Handwashing is a critical deterrent to the transmission of infectious organisms. Handwashing should be encouraged after using the toilet and immediately before eating. Handwashing is essential before and after any situation when hands might come in direct contact with blood, human or animal body secretions, and excretions. The importance of handwashing cannot be undermined by the belief that it is impractical. Adequate handwashing facilities must be available at all times. Good handwashing includes the following procedures:
- Ensure that each hand sink is supplied with dispensed soap and disposable paper towels.
- Alcohol-based (at least 60% ethanol or at least 70% isopropanol) hand sanitizer should be provided where water is not available. Hand sanitizer should not be used instead of handwashing when hands are visibly dirty, greasy, or sticky.
- Wet hands thoroughly with running water.
- Dispense soap into wet hands; bar soap may be used if dispensed soap is unavailable.
- Lather soap by vigorously rubbing hands together for at least 20 seconds, paying particular attention to the backs of the hands, nails, cuticles, spaces between the fingers, and under jewelry.
- Wash hands above the wrist level.
- Rinse hands thoroughly.
- Dry hands using a disposable paper towel; avoid the use of common towels.
- Use the paper towel to turn off the water.
- Dispose of the paper towel in a waste receptacle.
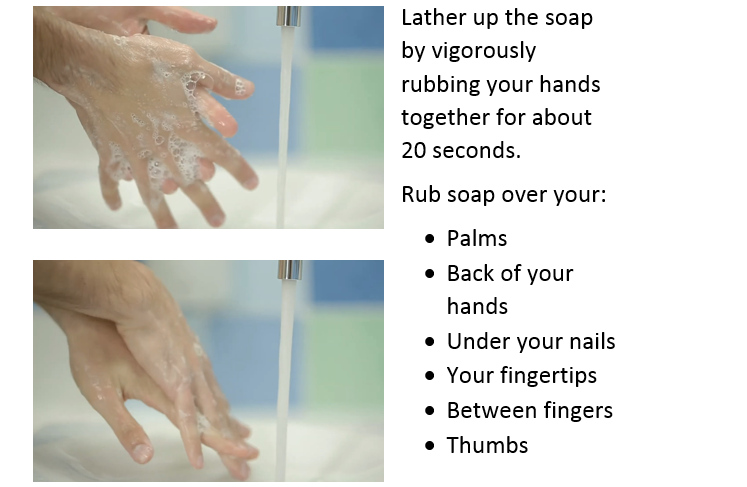
When washing your hands, you can use any hand soap with clean water. Antibacterial soap is not needed, and any temperature water is okay. Hot water is not needed or recommended because it can cause excessive hand dryness. To wash your hands:
- Step 1: Wet hands thoroughly with clean, running water.
- Step 2: Dispense soap into your wet hands. If you are using a bar of soap, do not share that soap with others.
- Step 3: Lather up the soap by vigorously rubbing your hands together for at least 20 seconds, paying particular attention to the backs of the hands, fingertips, under the nails, cuticles, spaces between the fingers, and under jewelry. Make sure you wash above the wrist level and also include your thumbs. It is important to wash your hands for at least 20 seconds to ensure you thoroughly clean all surfaces of your hands. Try humming the 'Happy Birthday' song twice while you wash your hands to make sure it takes at least 20 seconds.
- Step 4: Rinse your hands thoroughly with clean, running water.
- Step 5: Dry your hands using a disposable paper towel. You may use the paper towel to turn off the faucet, but this is not necessary. Avoid the use of shared towels.



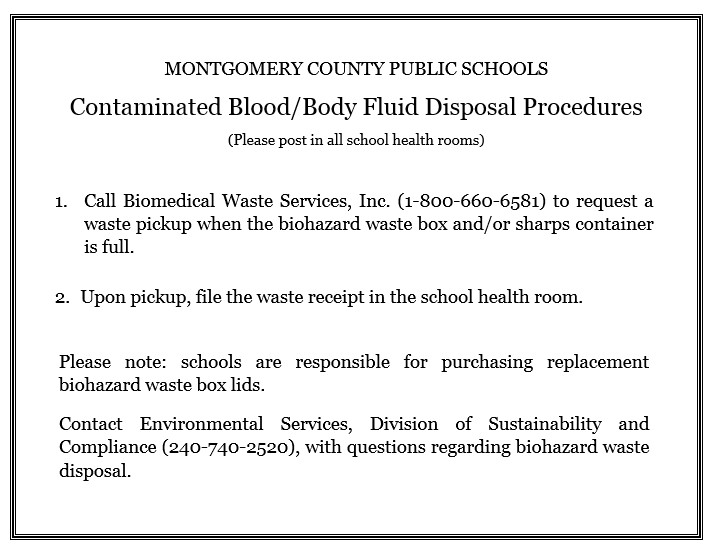
Biohazard Waste, Sharps Containers
Each school health room has a biohazard waste box and lid with red biohazard bag. A sign titled, Contaminated Blood/Body Fluid Disposal Procedures, is posted above the box (replacement signs may be downloaded here: Biohazard waste sign. Biomedical Waste Services (the MCPS contractor for biohazard waste removal) can be reached at 1-800-660-6581 to request a pickup when the biohazard container and/or sharps container is full. Division of Sustainability and Compliance pays for pick-up and replacement of biohazard boxes and sharps containers, but schools are responsible for purchasing replacement biohazard box lids.
All used medical sharps (including syringes, needles, lancets, auto injectors) must immediately be discarded in sharps containers. School employees with used sharps must work with their school health rooms to ensure safe disposal in sharps containers. Sharps must never be placed in the trash or toilets. Sharps must always be stored safely and securely - they may not be left in drawers, closets, cabinets, or other areas where they can cause injury.
If you have questions or need assistance related to biohazard waste boxes and sharps containers, please contact Mr. Brian Mullikin, Team Leader, Environmental Services, Division of Sustainability and Compliance, at 240-740-2520 or via e-mail.
Each secondary school health room has been provided a claw grabber tool for safely picking up used syringes. A video and informational document describing how to use the tool to pick up syringes are below.
2023 0317 Claw Grabber One Pager.pdf 
Cleaning Procedures
Non-Porous Surfaces (floors, walls, counter tops)
- Wear disposable nitrile gloves, goggles, and face mask and/or face shield. Wear additional PPE (such as a gown or apron), as needed, to prevent exposure to body fluids.
- Keep unauthorized people away from the contaminated area.
- Contact the facility's maintenance and operations service center for assistance, as needed, if large areas are heavily contaminated.
- Wipe the surface clean with a paper towel. Clean the surface with an MCPS-approved cleaning product or cleaning/disinfectant product, as needed.
- Disinfect the surface with a germicidal solution. Use 10% bleach solution (1 part bleach, 9 parts water), properly-diluted 3M #5L Quat disinfectant, Lysol Brand II disinfecting wipes, Clorox Commercial Solutions disinfecting wipes, Safetec SaniZide Plus germicidal solution, or other MCPS-approved disinfectant product. Bleach solution may only be used at locations where an eyewash station is available and by employees who have been trained to use it. Never mix different disinfectant or cleaning products.
- Keep the surface wet with the disinfectant for the manufacturer-recommended contact time to effectively kill infectious agents. Re-apply disinfectant, if needed, to keep the surface wet for the full contact time. Contact times are:
- 10 minutes for bleach solution (use within 24 hours of preparation; for use only by employees trained to use bleach; may only be used at locations where an eyewash station is available)
- 10 minutes for 3M #5L Quat
- 4 minutes for Lysol Brand II disinfecting wipes
- 1 minute for Diversey Oxivir Tb wipes
- 4 minutes for Clorox Commercial Solutions disinfecting wipes
- 5 minutes for Safetec SaniZide Plus germicidal solution
- Use tools, such as disposable scoops from a bloodborne pathogen spill kit, as much as possible to handle materials instead of using hands (even with gloves on). Disposable tools should be discarded and reusable tools should be cleaned and disinfected using the provided procedure for cleaning objects.
- Dispose of contaminated materials and disposable PPE in a lined waste container. Clean and disinfect reusable PPE and tools.
- Draw the plastic liner out of the waste container, tie, and immediately discard. Place waste that is visibly contaminated with body fluids in the cardboard biohazard waste box located in the school health room.
- Remove PPE in this order:
- Remove gloves first, and then wash hands.
- Remove gown or apron (if worn), and then wash hands if visibly contaminated.
- Remove face shield (if worn) and goggles, and then wash hands if visibly contaminated.
- Remove face mask (if worn).
- Wash hands.
- Wear disposable nitrile gloves, goggles, and face mask and/or face shield. Wear additional PPE (such as a gown or apron), as needed, to prevent exposure to body fluids.
- Discard contaminated objects that cannot be cleaned (such as porous materials that cannot be laundered) in the cardboard biohazard waste box located in the school health room.
- Clean the object using an MCPS-approved cleaning product or cleaning/disinfectant product. Soap and water may be used, as appropriate. Use paper towels to wipe, as needed.
- Disinfect with a germicidal solution. Use 10% bleach solution (1 part bleach, 9 parts water), properly-diluted 3M #5L Quat disinfectant, Lysol Brand II disinfecting wipes, Clorox Commercial Solutions disinfecting wipes, Safetec SaniZide Plus germicidal solution, or other MCPS-approved disinfectant product. Bleach solution may only be used at locations where an eyewash station is available and by employees who have been trained to use it. Never mix different disinfectant or cleaning products.
- To effectively kill infectious agents, keep the object wet with disinfectant for the manufacturer-recommended contact time. Re-apply disinfectant, if needed, to keep the surface wet for the full contact time. Contact times are:
- 10 minutes for bleach solution (use within 24 hours of preparation; for use only by employees trained to use bleach; may only be used at locations where an eyewash station is available)
- 10 minutes for 3M #5L Quat
- 4 minutes for Lysol Brand II disinfecting wipes
- 1 minute for Diversey Oxivir Tb wipes
- 4 minutes for Clorox Commercial Solutions disinfecting wipes
- 5 minutes for Safetec SaniZide Plus germicidal solution
- Keep the objects away from unauthorized people while cleaning and disinfecting.
- Objects that might be placed in a person's mouth of have prolonged contact with skin or other exposed body surface should be rinsed thoroughly with clean water after disinfection.
- Dispose of contaminated materials and disposable PPE in a lined waste container. Clean and disinfect reusable PPE and tools.
- Draw the plastic liner out of the waste container, tie, and immediately discard. Place waste that is visibly contaminated with body fluids in the cardboard biohazard waste box located in the school health room.
- Remove PPE in this order:
- Remove gloves first, and then wash hands.
- Remove gown or apron (if worn), and then wash hands if visibly contaminated.
- Remove face shield (if worn) and goggles, and then wash hands if visibly contaminated.
- Remove face mask (if worn).
- Wash hands.
- Ensure exposed individuals receive first aid, if needed. Request assistance from health room staff or call 911, as needed.
- Wear disposable nitrile gloves, goggles, and face mask and/or face shield. Wear additional PPE (such as a gown or apron), as needed, to prevent exposure to body fluids.
- Use a paper towel to wipe material from exposed skin, paying particular attention to the face. Allow person to rinse mouth, nose, and eyes with running water, if feasible. Place soiled towels in a lined waste container.
- If feasible, remove soiled clothing and place in a plastic bag for laundering at a later time. Assist in the cleansing of the affected body area. Put on clean clothing and/or notify parent or guardian. Soiled clothing should be laundered separately from the rest of the laundry. Use hot water and a cup of bleach in each load.
- Do not apply disinfectant solution to body surfaces. Request assistance from health room staff or medical personnel, as needed.
- For assistance with runny nose, coughing, and/or drooling, provide facial tissues and discard in a plastic-lined trash can.
- Dispose of contaminated materials and disposable PPE in a lined waste container. Clean and disinfect reusable PPE.
- Draw the plastic liner out of the waste container, tie, and immediately discard. Place waste that is visibly contaminated with body fluids in the cardboard biohazard waste box located in the school health room.
- Remove PPE in this order: