 MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS
MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS
MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS
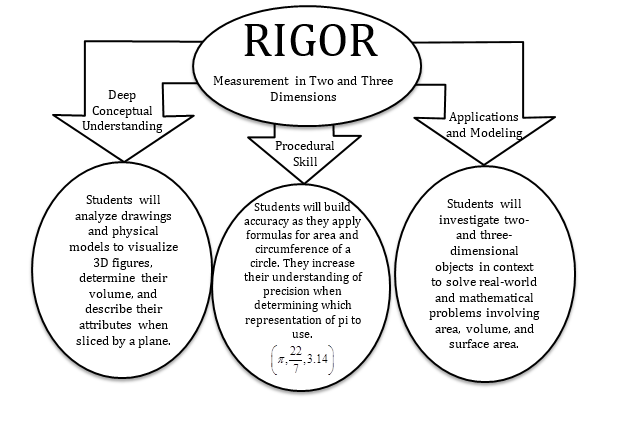
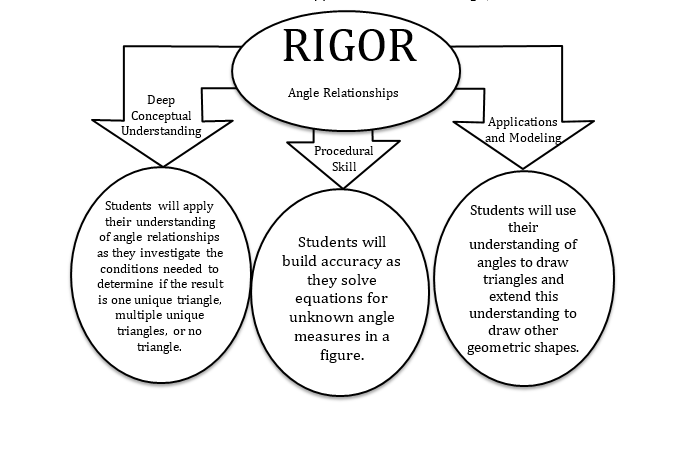
The Common Core State Standards require a balance of three fundamental components that result in rigorous mathematics acquisition: deep conceptual understanding, procedural skill, and mathematical applications and modeling.
Draw (freehand, with ruler, and with technology) geometric shapes with given conditions.
Draw a segment AB 1 cm. in length. Draw a circle whose radius is segment AB.
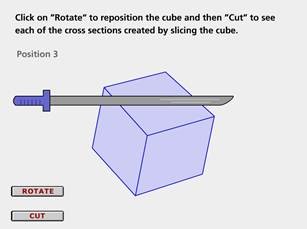
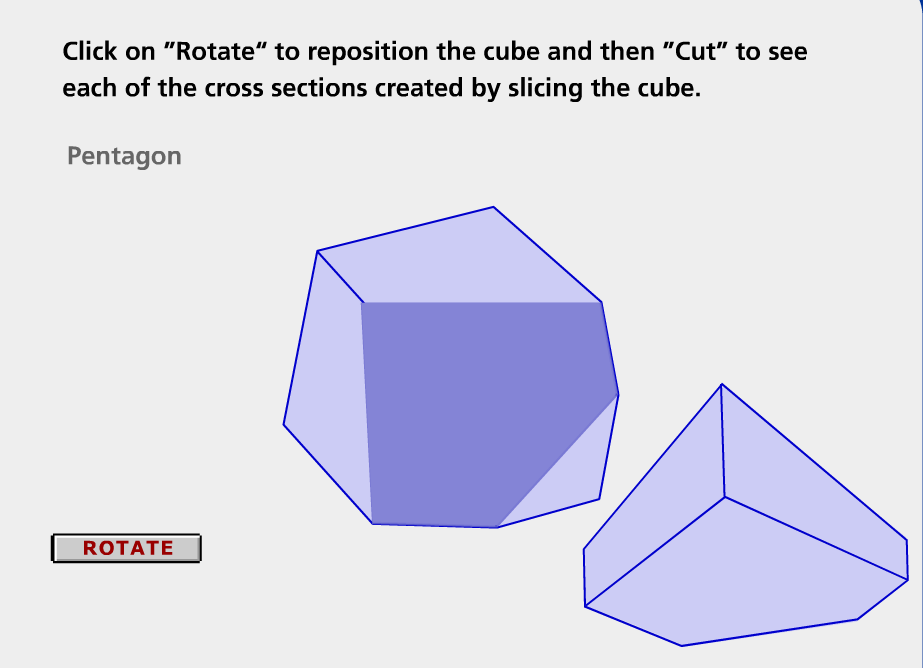
Describe the two-dimensional figures that result from slicing three-dimensional figures, as in plane sections of right rectangular prisms and right rectangular pyramids.
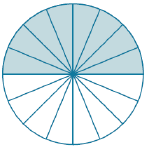
Know the formulas for the area and circumference of a circle and use them to solve problems; give an informal derivation of the relationship between the circumference and area of a circle.
Describe how the two illustrations can be used to describe the relationship between the area and circumference of a circle.
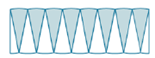
Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, volume and surface area of two- and three-dimensional objects composed of triangles, quadrilaterals, polygons, cubes, and right prisms.
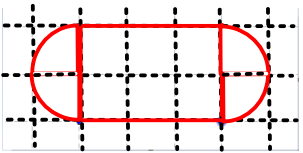
Draw (freehand, with ruler, and with technology) geometric shapes with given conditions.
Investigate automotive brand logos that are composed of polygons and circles. Practice measuring and drawing the logos using everyday tools, such as rulers and string


Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving surface area of two-dimensional objects composed of triangles, quadrilaterals, polygons, and circles.
For example, examine the shape of a landscaped flowerbed. Determine the shapes that compose the figure. Discuss the strategy that can be used to determine the area of the flowerbed.
*Additional Practice links support C2.0 content, but may use vocabulary or strategies not emphasized by MCPS.
*Instructional videos in the hyperlinks above are meant to support C2.0 content, but may use vocabulary or strategies not emphasized by MCPS.
The Common Core State Standards require a balance of three fundamental components that result in rigorous mathematics acquisition: deep conceptual understanding, procedural skill, and mathematical applications and modeling.
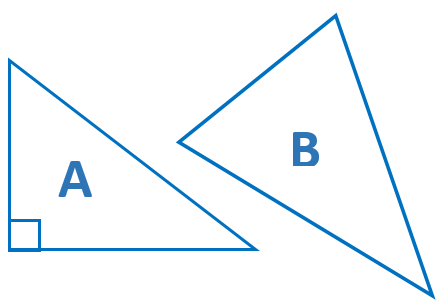
Draw (freehand, with ruler and protractor, and with technology) geometric shapes with given conditions. Focus on constructing triangles from three measures of angles or sides, noticing when the conditions determine a unique triangle, more than one triangle, or no triangle.
Use your protractor to measure the angles of triangles A and B. Use your ruler to measure the side lengths of triangles A and B (in cm). Label the angle measures and side lengths.
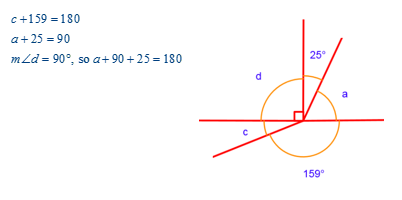
Use facts about supplementary, complementary, vertical, and adjacent angles in a multi-step problem to write and solve simple equations for an unknown angle in a figure.
Write and solve equations to determine the unknown angle measures below:
Investigate a local street system design using a street map or by visiting Google© maps.
Angle Relationships: complementary and supplementary angles (online matching game)
*Additional Practice links support C2.0 content, but may use vocabulary or strategies not emphasized by MCPS.
IM 6–8 Math was originally developed by Open Up Resources and authored by Illustrative Mathematics, and is copyright 2017-2019 by Open Up Resources. It is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0). OUR's 6–8 Math Curriculum is available at https://openupresources.org/math-curriculum/.